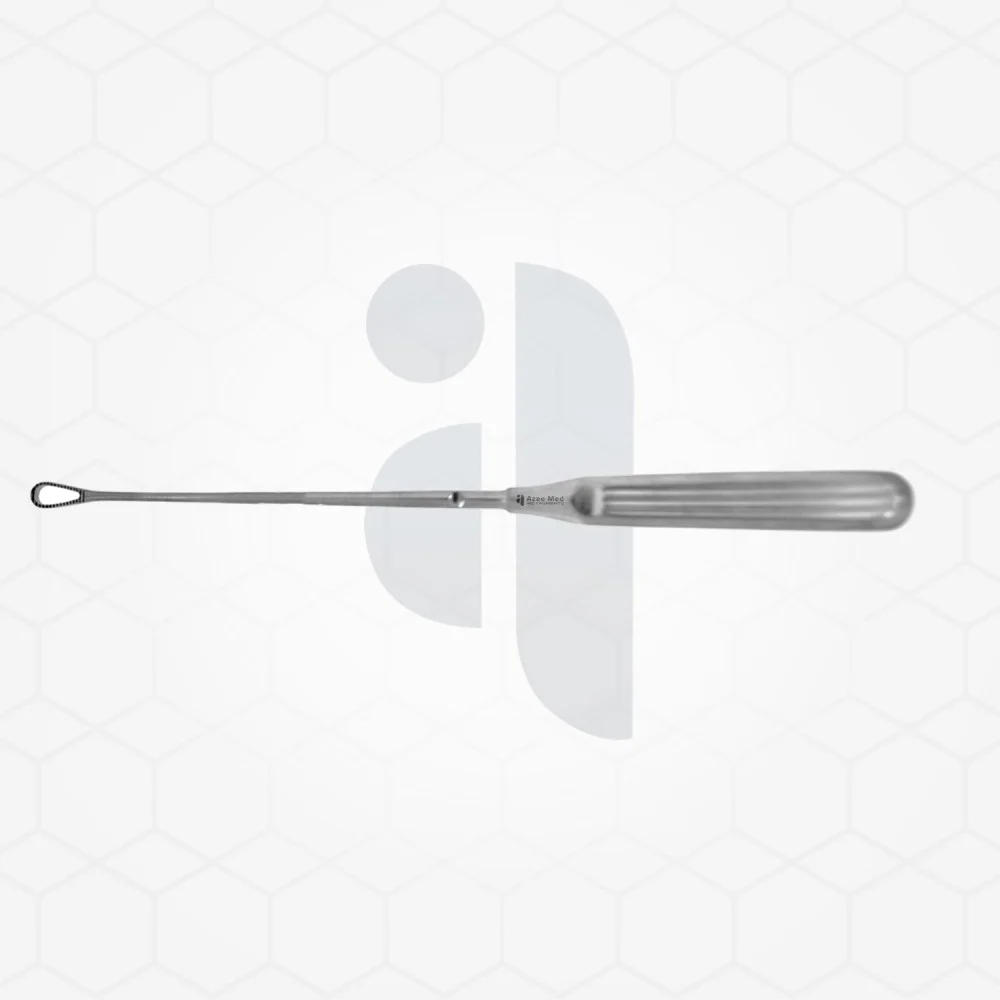
Adenoidectomies remain one of the most common surgical procedures performed in pediatric otolaryngology. Success in these delicate operations relies heavily on the surgeon's skill and the quality of their instrumentation. A specialized tool like an adenoid curette allows for the precise removal of adenoid tissue while minimizing trauma to surrounding structures. Azeemed Instruments is dedicated to providing high-quality surgical tools that meet the needs of professionals, ensuring that every procedure is supported by reliable, precision-crafted equipment. This guide explores the design, function, and best practices for utilizing this essential instrument in modern surgery.

Understanding the Design and Functionality
The design of a surgical instrument dictates its effectiveness in the operating room. An adenoid curette typically features a sharp, fenestrated basket attached to a slender shaft, which allows surgeons to scrape away adenoid tissue from the nasopharynx effectively. The curvature of the shaft is engineered to navigate the unique anatomy of the upper throat without causing unnecessary damage. Surgeons prefer this manual tool because it offers tactile feedback that powered instruments sometimes lack. This feedback is crucial for determining exactly how much tissue needs to be removed and for ensuring that the underlying muscle remains intact.
High-quality steel construction ensures the blade maintains its sharpness over repeated sterilizations. A dull instrument can lead to incomplete tissue removal or excessive bleeding, complicating the recovery process for the patient. Azeemed Instruments understands these critical requirements and manufactures tools that maintain their integrity procedure after procedure. By prioritizing durability and ergonomic design, we help surgeons maintain control and comfort during what can be a repetitive motion.
Preparing the Surgical Field for Optimal Access
Accessing the surgical site is the first hurdle in any successful adenoidectomy. Before the surgeon can effectively employ the curette, the patient's mouth must be held open securely and safely. This is where a gagged mouth instrument, such as a Boyle-Davis mouth gag, becomes indispensable. This device retracts the tongue and keeps the jaw open, providing a clear and unobstructed view of the posterior pharynx. Proper exposure is critical; without it, even the most skilled surgeon cannot safely navigate the delicate structures of the throat. Once the field is clear and stable, the surgeon can introduce the curette with confidence.
Proper positioning of the patient also plays a significant role. The neck is usually extended to bring the adenoids into better view. The combination of optimal patient positioning and reliable retraction tools sets the stage for a smooth operation. Surgeons rely on this setup to prevent accidental injury to the lips, teeth, or tongue while focusing entirely on the adenoid bed.
Techniques for Effective Tissue Removal
Using an adenoid curette requires a specific technique to ensure safety and efficacy. The standard motion involves a single, sweeping stroke from the superior aspect of the adenoid pad down toward the pharynx. This motion shears the adenoid tissue from the posterior pharyngeal wall. It is essential to engage the tissue firmly but gently. If the surgeon applies too much pressure, they risk injuring the prevertebral fascia; too little pressure may result in leaving residual tissue behind, which can lead to symptom recurrence.
Experienced practitioners often palpate the area after the initial curettage. This tactile check confirms that the choanae are patent and that no obstructive tissue remains. Occasionally, a smaller curette may be needed to reach lateral bands of lymphoid tissue near the Eustachian tube orifices. Precision here is vital to prevent future ear infections or hearing issues caused by blocked tubes. Azeemed Instruments offers various sizes of curettes to accommodate different anatomical needs, ensuring that surgeons have the right tool for every patient, from toddlers to older children.
Post-Operative Care and Instrument Maintenance
After the procedure is complete, the focus shifts to hemostasis and patient recovery. While the adenoid curette is designed to minimize bleeding by making clean cuts, some oozing is inevitable. Surgeons typically use suction diathermy or packing to control this. The clean cut provided by a sharp, well-maintained instrument significantly aids the natural clotting process. A ragged cut from an inferior tool would result in more tissue trauma and a longer healing time for the young patient.
Caring for the surgical instruments is just as important as the surgery itself. Thorough cleaning and sterilization protocols extend the life of the adenoid curette and ensure patient safety. Biological debris must be completely removed from the basket and fenestrations before autoclaving. Regular inspection for burrs or dullness on the blade edge is standard practice for surgical teams committed to excellence. Azeemed Instruments supports this lifecycle by providing tools crafted from corrosion-resistant materials that withstand rigorous sterilization cycles.
Why Quality Instrumentation Matters
The difference between a routine surgery and a complicated one often comes down to the reliability of the tools in hand. When a surgeon picks up an adenoid curette made by Azeemed Instruments, they trust that it will perform exactly as expected. This trust allows the medical professional to focus entirely on their technique and the patient's well-being rather than worrying about equipment failure. In the high-stakes environment of an operating room, consistency is invaluable.
Investing in high-quality surgical instruments is an investment in patient outcomes. Tools that are ergonomic, durable, and precise reduce surgeon fatigue and improve surgical accuracy. By choosing Azeemed Instruments, healthcare providers are partnering with a company that understands the nuance of surgical care. We remain committed to innovation and quality assurance, ensuring that every instrument we deliver contributes to a safer, more effective healthcare environment.