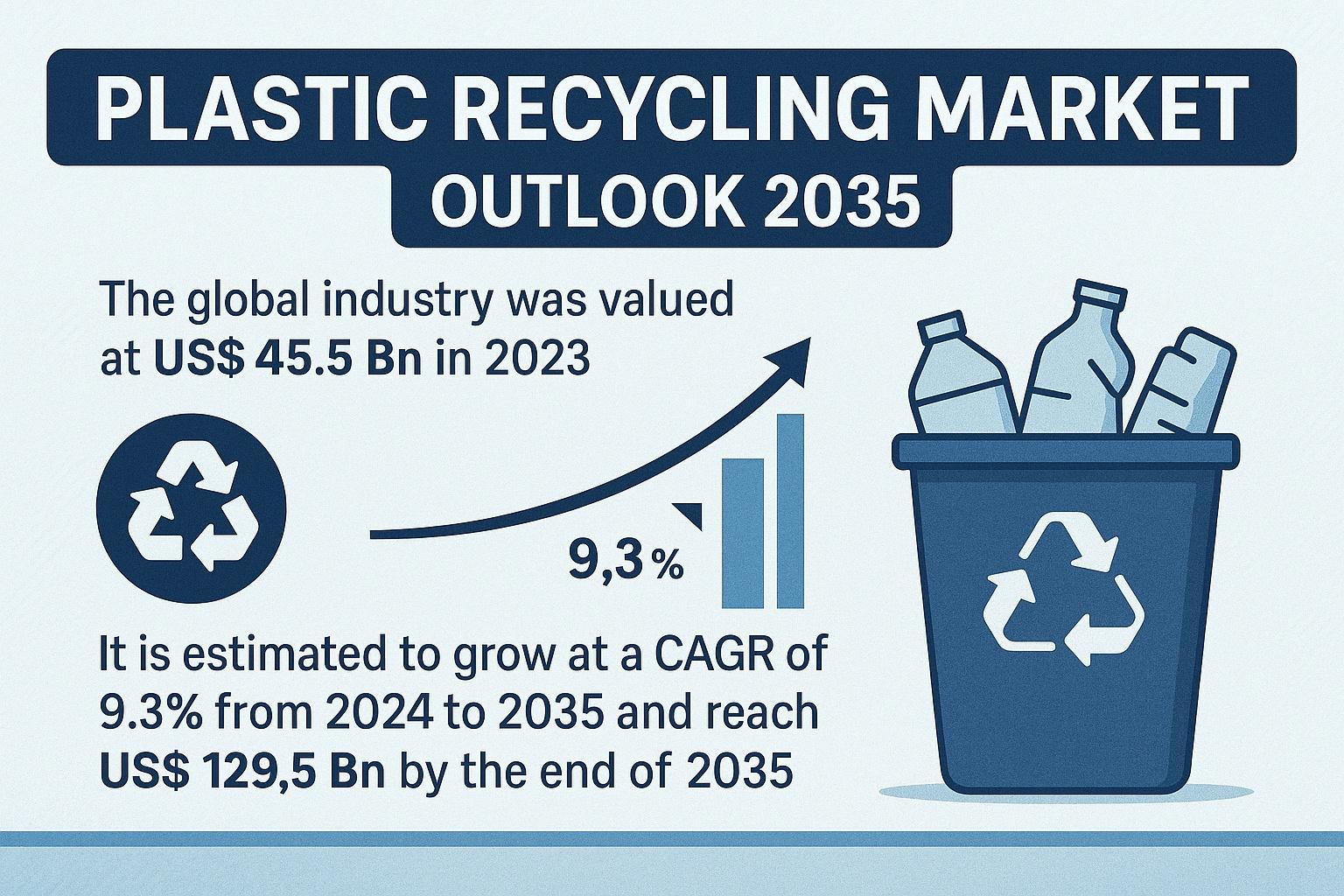
The Plastic Recycling Market has become one of the most critical components of global sustainability initiatives, driven by increasing environmental concerns, corporate responsibility mandates, and stringent government regulations aimed at tackling plastic waste. With the market valued at US$ 45.5 Bn in 2023, it is expected to expand at a CAGR of 9.3% from 2024 to 2035, climbing to US$ 129.5 Bn by the end of 2035. This robust growth is supported by rapid advancements in recycling technologies, rising adoption of recycled plastics across industries, and the increasing momentum of circular economy principles worldwide.
The market landscape is transitioning from traditional mechanical recycling to high-efficiency methods powered by artificial intelligence, near-infrared sorting systems, and chemical recycling breakthroughs. At the same time, evolving consumer preferences for eco-friendly products and global movements against single-use plastics are significantly influencing purchasing behaviors and industrial production processes. As a result, plastic recycling is no longer a waste management option but a strategic necessity for manufacturers, governments, and consumers.
1. Introduction
Plastic pollution has become a defining environmental challenge of the 21st century. With millions of tons of plastic entering oceans and landfills each year, governments and global organizations are ramping up efforts to promote recycling, reduce virgin plastic consumption, and encourage sustainable material cycles. The Plastic Recycling Market is central to these efforts.
This article explores the key forces shaping the global market, technological advancements, segmentation insights, regional opportunities, and competitive dynamics that define the industry's future trajectory. It also sheds light on how regulatory policies and innovation are accelerating the adoption of recycled plastics across consumer and industrial applications.
2. Market Definition and Scope
The plastic recycling market includes the collection, sorting, processing, and conversion of plastic waste into usable raw materials. These recycled materials are then utilized in applications such as packaging, automotive components, textiles, construction materials, and household goods.
The scope encompasses:
-
Post-consumer plastic waste
-
Post-industrial scrap
-
Mechanical, chemical, and hybrid recycling technologies
-
Material recovery systems and plastic-to-fluid conversion technologies
-
Food-grade and non-food-grade recycled resin production
The overarching goal is to minimize reliance on virgin plastic, maximize resource efficiency, and promote circularity in the global plastic value chain.
3. Market Dynamics
3.1 Key Drivers
A. Regulatory Push for Sustainable Plastic Management
Governments worldwide have enacted stringent policies to curb plastic waste leakage into landfills and natural ecosystems. These include:
-
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) mandates
-
Bans on single-use plastics
-
Mandatory recycling quotas
-
Plastic taxes and eco-modulated fees
Such regulations significantly boost recycling demand and encourage companies to integrate recycled content into their products.
B. Increasing Global Awareness of Plastic Pollution
Consumers are more conscious of the environmental harm caused by plastics. This awareness is influencing purchasing patterns, with demand rising for sustainably packaged goods. As a result, companies are increasing their use of recycled materials to maintain brand loyalty and adhere to sustainability commitments.
C. Economic Benefits of Recycling
Recycling plastics reduces dependence on crude oil—an essential raw material in virgin plastic production. In fact, 1000 kg of recycled plastic saves 685 gallons of oil and 5800 kWh of energy, making recycled polymers a financially viable and environmentally superior alternative.
D. Technological Advancements in Sorting & Processing
Modern recycling systems now employ:
-
Robotics and AI-based recognition
-
Near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy
-
Hyperspectral imaging
-
Optical sorting and automated conveyor systems
These innovations enhance efficiency, reduce contamination, and improve output quality.
3.2 Market Restraints
-
Lack of standardized waste segregation in many regions
-
High initial investment for advanced recycling setups
-
Lower performance of certain recycled materials vs. virgin plastics
-
Limited chemical recycling facilities in developing economies
3.3 Opportunities
-
Rising demand for rPET in beverage packaging
-
Increasing use of recycled plastics in EV manufacturing
-
Corporate commitments to 100% recyclable packaging
-
Rapid growth of biodegradable and bio-based plastic blends
-
Investment in advanced chemical recycling that allows multilayered and composite plastics to be processed
3.4 Trends Shaping the Market
-
Global shift toward circular economy principles
-
Strong growth of deposit return schemes (DRS)
-
Recycled materials gaining traction in fashion and sportswear
-
Increasing adoption of blockchain to track plastic waste streams
-
Rapid expansion of urban mining and recovery systems
4. Market Segmentation
4.1 By Product Type
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
A highly recycled polymer used in beverage bottles, food containers, and textiles. Strong global demand for rPET contributes to its rapid market expansion.
PP (Polypropylene)
Used widely in packaging, automotive, and household products. Technological improvements are boosting its recyclability.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) – Leading Segment
HDPE’s dominance is driven by its durability, chemical resistance, and ease of recycling.
Key features include:
-
Ability to withstand multiple processing cycles
-
High applicability across bottles, packaging, pipes, and automotive parts
-
Increasing preference for rHDPE in detergent and milk bottles
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene)
Commonly used in bags and films. Enhanced recovery technologies are improving LDPE recycling rates.
PS and PVC
Historically difficult to recycle due to structural instability and harmful additives. Recent chemical recycling developments have begun to support their recovery.
Others
Includes engineering plastics, bio-based blends, and multi-layered materials.
4.2 By Application
A. Packaging – Dominant and Fastest-Growing Segment
Packaging accounts for the largest share of plastic usage globally, making it the biggest contributor to the recycling stream. The rise of e-commerce, FMCG expansion, and global food distribution networks drive significant plastic consumption.
B. Automotive
Automakers increasingly incorporate recycled plastics to meet sustainability targets. Use cases include interiors, bumpers, trims, and insulation.
C. Construction
Recycled plastics are used for pipes, decks, insulation materials, roofing sheets, and panels.
D. Textiles
rPET-based polyester has become a mainstream material in apparel, footwear, and furnishings.
E. Others
Includes electronics, agriculture, furniture, and industrial applications.
5. Regional Market Insights
Asia Pacific – Market Leader
Asia Pacific dominates due to:
-
Massive production and consumption of plastics
-
Large-scale industrialization
-
Huge population and growing middle class
-
Expanding recycling capacity
-
Increasing public awareness of pollution
China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asian countries drive significant market growth.
North America
A highly organized recycling industry supported by policy initiatives and technological innovation. The region is witnessing increased investment in chemical recycling and waste-to-fuel technologies.
Europe
One of the strictest regulatory environments globally. The EU’s Green Deal and waste framework directives propel recycling adoption. Europe also leads in deposit return schemes and closed-loop recycling.
Latin America
Improving regulatory landscape and growing participation of private recycling companies. Brazil and Mexico remain key contributors.
Middle East & Africa
Early stage but rapidly developing market with rising investments in waste management infrastructure.
6. Competitive Landscape
The market is highly fragmented, with both global and regional players shaping the competitive ecosystem. Companies are focusing on capacity expansion, innovation, partnerships, and improved processing technologies.
Key Players Include:
-
Kuusakoski
-
B&B Plastics Inc.
-
Custom Polymers, Inc.
-
Dart Container Corporation
-
Novolex
-
KW Plastics
-
MBA Polymers UK Ltd.
-
PLASgran Ltd.
-
Plastipak Holdings, Inc.
-
WM Recycle America LLC
-
Wellpine Plastic, LTD
-
Others
Key Growth Strategies
-
Mergers & acquisitions
-
Expansion into food-grade recycled plastics
-
Technological modernization
-
Strategic collaborations
-
Supply chain strengthening
7. Recent Industry Developments
-
April 2023: Indorama Ventures and Evertis collaborated to produce PET films using recycled PET tray flakes, supporting Evertis’ goal of 50% recycled content by 2025.
-
February 2023: Loop Industries, SUEZ, and SK geo centric selected the Grand Est region in France for a plant designed to produce virgin-quality PET using 100% recycled feedstock.
-
November 2022: Plastipak Holdings launched a new rPET recycling facility in Toledo, Spain, for producing food-grade recycled pellets.
8. Market Outlook 2024–2035
As sustainability regulations tighten and corporate commitments to 100% recyclable packaging strengthen, the demand for recycled plastics will continue to surge. Key trends shaping future growth include:
-
AI-driven, automated recycling plants
-
Expansion of chemical recycling technologies
-
Higher adoption of food-grade recycled polymers
-
Strong public pressure against single-use plastics
-
Increased investment in circular economy projects
With Asia Pacific leading global consumption and Europe driving regulatory transformation, the market is expected to witness significant advancements and large-scale capacity expansions. Companies investing in advanced recycling technologies and circular business models will be best positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Conclusion
The Plastic Recycling Market is at the forefront of global sustainability transformation. Backed by rising environmental consciousness, regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and strong industry collaborations, the market offers immense opportunities for both established players and emerging innovators. As recycling technologies evolve and consumer demand for eco-friendly products intensifies, the industry will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable, circular global economy.