Introduction:
In business, technology, and everyday operations, efficiency is a key factor for achieving success. However, even the most well-designed systems can run into obstacles that slow progress. One of the most common issues faced in production, workflow, or digital processing is known as a bottleneck. A bottleneck occurs when one part of a system is slower or less efficient than the parts before or after it, causing delays, reduced output, and decreased productivity.
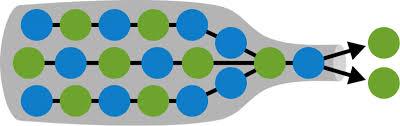
The term “bottleneck” comes from the shape of a bottle: while the main body is wide and spacious, the neck is narrow, restricting flow. Similarly, in processes, a bottleneck limits how fast work can pass through a system. Identifying and addressing bottlenecks is necessary for improving performance in business, manufacturing, computing, and daily tasks.
What Is a Bottleneck?
A bottleneck is a point in a workflow where the capacity is limited compared to the rest of the system. This limitation causes slowdowns, backlogs, and inefficiencies. Bottlenecks can occur in both physical systems (like production lines) and digital systems (such as computing or data processing).
For example:
-
In a factory, if one machine operates slower than others, production will pile up at that machine.
-
In computing, if a CPU can process data faster than the RAM or storage can supply it, the overall speed slows down.
-
In businesses, if one department takes longer to complete tasks, it delays the entire project timeline.
Common Causes of Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks can happen for several reasons, including:
1. Lack of Capacity
When one part of the system is not capable of handling the required workload.
2. Poor Resource Allocation
If employees, tools, or time are not distributed efficiently, workflow becomes uneven.
3. Outdated Technology
Old equipment or software may not keep up with current demand.
4. Complex Procedures
Manual steps or unnecessary tasks can slow down operations.
5. Skills Gaps
Workers may require additional training to complete tasks effectively and quickly.
See more: Bottleneck Rechner
Examples of Bottlenecks in Different Fields
In Manufacturing
A slow assembly station or a malfunctioning machine can delay the entire production line.
In Business Administration
Slow approval processes or communication gaps between departments can stall progress.
In Computing
A bottleneck can occur when a computer’s processor, memory, or graphics card cannot keep up with other components, leading to reduced system performance.
In Logistics
If a delivery truck can't carry enough goods, shipping delays and increased costs follow.
Effects of Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks have several negative impacts:
-
Reduced productivity
-
Customer dissatisfaction due to delays
-
Increased operational costs
-
Employee stress and frustration
-
Lower profitability
Even a small bottleneck, if left unresolved, can cause large-scale inefficiencies.
How to Identify a Bottleneck
Identifying the bottleneck is the first step toward solving it. Some ways to detect bottlenecks include:
-
Monitoring workflow over time
-
Analyzing output rates of each step in a process
-
Gathering team feedback on delays or common problems
-
Using performance tracking software or diagnostic tools in digital systems
Look for steps where work accumulates, slows down, or stops entirely.
Solutions to Reduce or Eliminate Bottlenecks
Once identified, bottlenecks can often be solved through:
1. Increasing Capacity
Add additional machines, employees, or resources to match demand.
2. Automation
Automate repetitive tasks to speed up workflow.
3. Training
Provide skill development to improve performance and reduce errors.
4. Upgrading Technology
Modern tools enhance efficiency and reliability.
5. Process Optimization
Remove unnecessary steps and simplify procedures to improve flow.
Solving a bottleneck leads to smoother operations and higher productivity.
Conclusion
A bottleneck may seem like a small issue at first, but its effects can ripple across entire systems, affecting productivity, efficiency, and profitability. Whether in manufacturing, computing, business management, or daily tasks, identifying and resolving bottlenecks is essential for improving performance. By analyzing workflows, upgrading resources, and optimizing processes, organizations can enhance output and reduce delays. Understanding and addressing bottlenecks not only strengthens operations but also contributes to long-term success and growth.
See more blogs: Visit Here