The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) stands as one of the most ambitious infrastructure and development projects in South Asia. Initiated under China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), CPEC connects western China with Pakistan’s Gwadar Port, creating a strategic trade and logistics network. Beyond its economic and commercial significance, the corridor has become a symbol of regional cooperation, attracting international investment and attention. Over the years, it has transformed Pakistan’s economic landscape by enhancing industrial productivity, modernizing transport infrastructure, and fostering energy development.
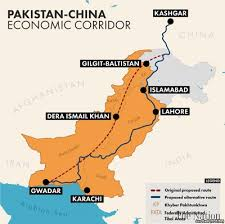
CPEC is much more than a collection of roads, railways, and ports. It represents a long-term vision to strengthen Pakistan’s industrial and commercial sectors while providing opportunities for employment, urban development, and technological advancement. By improving connectivity within Pakistan and linking it with international markets, CPEC is helping the country establish a strong foundation for sustainable economic growth and regional influence.
Is CPEC Driving Economic and Industrial Growth?
CPEC has emerged as a key driver of Pakistan’s economic development. The corridor’s energy projects, including coal, hydropower, and renewable energy plants, address one of Pakistan’s long-standing challenges—power shortages. A stable energy supply is essential for industries, manufacturing units, and urban infrastructure, enabling smooth operations and attracting foreign investment.
The development of Gwadar Port is central to this economic transformation. Strategically located near the Arabian Sea, Gwadar provides Pakistan with direct access to international trade routes, reducing shipping times for imports and exports. Combined with newly constructed highways and railways, the port facilitates efficient transportation of goods across Pakistan, lowering operational costs and encouraging industrial expansion.
Special economic zones (SEZs) established along the corridor further enhance industrial productivity. These zones attract both domestic and international investment, promote technology transfer, and generate employment for local communities. The corridor also stimulates growth in sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and services, creating a ripple effect that strengthens Pakistan’s overall economy.
CPEC’s influence is also felt in urban development and infrastructure modernization. Roads, bridges, and rail links connect previously isolated regions like Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa with major industrial and commercial centers, fostering inclusive growth. This connectivity improves supply chains, enhances trade efficiency, and allows small and medium-sized businesses to integrate into larger markets, making Pakistan a more competitive economy in the region.
Is CPEC Enhancing Regional Connectivity and Strategic Importance?
Beyond its domestic economic impact, CPEC plays a vital role in regional trade and connectivity. By linking western China to the Arabian Sea, the corridor provides China with a secure and shorter route for transporting goods and energy resources. This reduces reliance on traditional maritime channels such as the Strait of Malacca and enhances China’s trade resilience.
For Pakistan, improved transport infrastructure under CPEC strengthens regional trade links, facilitating cross-border commerce with Central Asia, the Middle East, and Africa. Industrial and logistics hubs along the corridor encourage foreign investment and promote collaborative business ventures. These developments also help Pakistan integrate less-developed areas into national and international trade networks, reducing economic disparities and supporting balanced regional growth.
CPEC also contributes to social and technological advancement. Industrial zones generate employment, while vocational training programs equip local communities with modern skills. Partnerships with Chinese enterprises introduce advanced manufacturing techniques, energy-efficient practices, and modern logistics solutions. Additionally, social infrastructure projects, including housing, healthcare, and education initiatives for workers, improve living standards and support inclusive development.
On a strategic level, CPEC strengthens Pakistan’s geopolitical relevance. By deepening ties with China, Pakistan positions itself as a key partner in the Belt and Road Initiative. The corridor enhances regional cooperation and creates opportunities for economic diplomacy, giving Pakistan leverage in both regional and international economic affairs. Sustainable energy projects and environmentally conscious industrial development further ensure that progress aligns with long-term social and environmental goals.
Conclusion
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor is a transformative initiative that is reshaping Pakistan’s economic, industrial, and strategic landscape. By fostering industrial growth, improving regional connectivity, creating employment, and supporting technological advancement, CPEC is helping Pakistan achieve sustainable development and enhanced global competitiveness.
While challenges such as security concerns, financing, and regional political dynamics remain, the corridor’s potential to strengthen Pakistan’s economy and elevate its strategic importance is undeniable. As infrastructure projects under CPEC continue to expand, they promise long-term benefits for businesses, local communities, and the nation as a whole. Understanding the scope and impact of CPEC is essential for investors, policymakers, and regional stakeholders aiming to participate in Pakistan’s evolving economic and strategic journey.


