Introduction
Allergies affect millions of people worldwide, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening reactions. Whether it's seasonal pollen, pet dander, food, or environmental triggers, identifying the root cause of allergic reactions is essential for effective management. This is where allergy testing comes in.
What Is Allergy Testing?
Allergy testing is a medical procedure used to determine what substances (called allergens) are triggering an allergic reaction in your body. These allergens could be found in:
- Foods (like peanuts, shellfish, dairy)
- Pollens (trees, grasses, weeds)
- Animal dander (cats, dogs, etc.)
- Mold
- Dust mites
- Medications or insect venom
By identifying specific allergens, doctors can help patients avoid them and recommend treatment options like medication, immunotherapy, or lifestyle changes.
Why Get Tested for Allergies?
1. Accurate Diagnosis
Symptoms like sneezing, coughing, rashes, or gastrointestinal upset can mimic other conditions. Allergy testing helps distinguish between true allergic responses and other health issues.
2. Targeted Treatment
Knowing your specific allergens allows doctors to tailor treatment plans—whether that means antihistamines, allergy shots, or dietary changes.
3. Improved Quality of Life
By identifying and managing allergies, you can enjoy daily activities without constant discomfort or fear of reactions.
4. Prevention of Severe Reactions
In cases of severe allergies, such as anaphylaxis (a life-threatening reaction), identifying and avoiding triggers could be lifesaving.
Types of Allergy Testing
There are several types of allergy tests. The best method for you depends on your symptoms, medical history, and the type of allergen suspected.
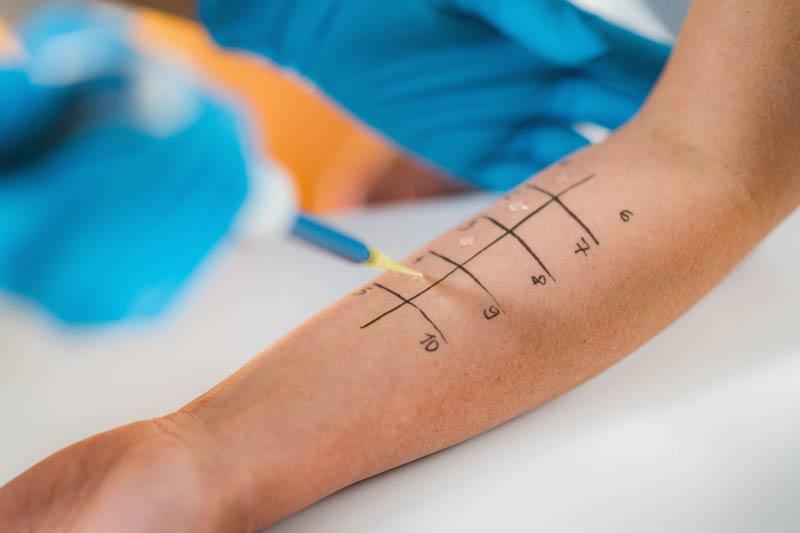
1. Skin Prick Test (SPT)
This is the most common type of allergy test. Tiny amounts of suspected allergens are pricked into the skin—usually on the forearm or back. If you’re allergic, a small raised bump (like a mosquito bite) will appear within 15–20 minutes.
- Best for: Pollen, pet dander, mold, dust mites, and some foods
- Quick results: Often within 30 minutes
- Low risk: Minimal discomfort and very safe
2. Intradermal Skin Test
In this method, a small amount of allergen is injected just under the skin. It's more sensitive than the skin prick test and is often used for detecting allergies to insect venom or medications.
3. Blood Tests (IgE Test)
Also known as the RAST or ImmunoCAP test, this measures the amount of Immunoglobulin E (IgE)—an antibody that increases in response to allergens—in your blood.
- Best for: Patients who can’t undergo skin testing (e.g., due to eczema, medication interference)
- Slower results: May take a few days
- More expensive than skin tests
4. Patch Testing
This test is used to detect delayed allergic reactions, usually to substances that touch the skin, like metals, fragrances, or latex. Patches with allergens are applied to the back and left in place for 48 hours.
- Best for: Contact dermatitis and skin allergies
Common Symptoms That May Require Allergy Testing
If you're experiencing any of the following symptoms frequently, allergy testing might be recommended:
- Chronic sneezing, runny nose, or congestion
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Persistent cough, wheezing, or asthma symptoms
- Skin rashes like hives or eczema
- Digestive issues (especially after eating certain foods)
- Headaches or fatigue during certain seasons
- Reactions after insect stings or taking medications
What to Expect During the Allergy Testing Process
- Initial Consultation – A healthcare provider will review your symptoms, medical history, and possible triggers.
- Test Selection – Based on your profile, your provider will choose the most appropriate test(s).
- Test Day – For skin tests, expect some mild discomfort. Blood tests are straightforward and quick.
- Results Review – Most skin test results are immediate, while blood tests may take a few days.
- Next Steps – Depending on the results, your doctor may recommend:
- Allergen avoidance strategies
- Medications (antihistamines, corticosteroids, nasal sprays)
- Allergy shots or oral immunotherapy for long-term relief
Allergy Management After Testing
Once your allergens are identified, effective management becomes much easier. Here’s how:
- Environmental Allergies: Use air purifiers, clean regularly, and avoid outdoor activities during high pollen times.
- Food Allergies: Carefully read food labels and inform restaurants of your allergies.
- Medication Allergies: Wear a medical alert bracelet and notify all healthcare providers.
- Insect Sting Allergies: Carry an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) if needed.
When Should You See a Specialist?
You should consider visiting an allergist or immunologist if:
- Over-the-counter treatments don’t relieve your symptoms
- You experience symptoms year-round
- You suspect a food allergy
- You've had a severe allergic reaction before
- You have asthma that worsens during allergy season
Final Thoughts
Allergy testing is a powerful tool that can uncover hidden triggers and help you reclaim your health. Whether you’re struggling with seasonal sniffles or suspect a more serious allergy, identifying the cause is the first step toward lasting relief.